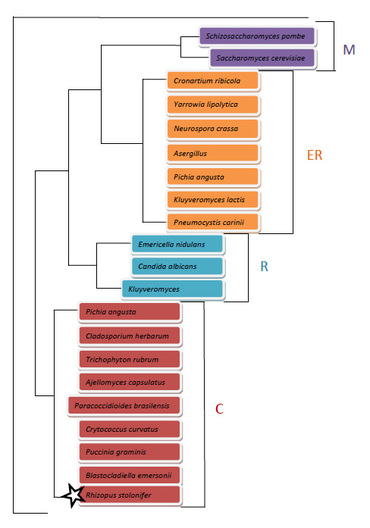
Phylogenetic tree composed by neighbor-joining different types of fungi by the location of fungal heat shock protein 70 (Hps70s) in their cells (1)
Description(1):
Habitat(1):
Description(1):
- Commonly known as black bread mold
- Filamentous mold
- Zygomycete
- Saprophytic: consumes dead organic matter
- Parasitic: absorbs all nutrients of substrate on which it lands
- Plays significant role in carbon cycle as a decomposer in the soil
- Grows primarily as mycelia that consists of hyphae that lack cross walls/ septa
- This means it is a coenocytic organism: multinucleate cell enclosed by one cell wall that contains chitin
Habitat(1):
- Spores are common and abundant in the air
- Able to quickly form on any surface where it can obtain food
- Commonly found in moist environments
- Also found in warm and dry environments like: soil, fresh decaying litter, wild bird nests, and children's sand boxes
 Rhizopus stolonifer growing on a casserole (1)
Rhizopus stolonifer growing on a casserole (1)
Nutrition(1):
- When comes in contact with a substrate, first spreads over surface and penetrates it while sending hyphae inward to absorb nutrients
- Dependent on sugar and starch, often found in bread and soft fruits
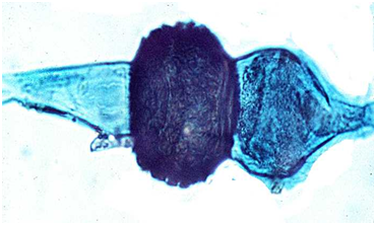 Zygospore (1)
Zygospore (1)
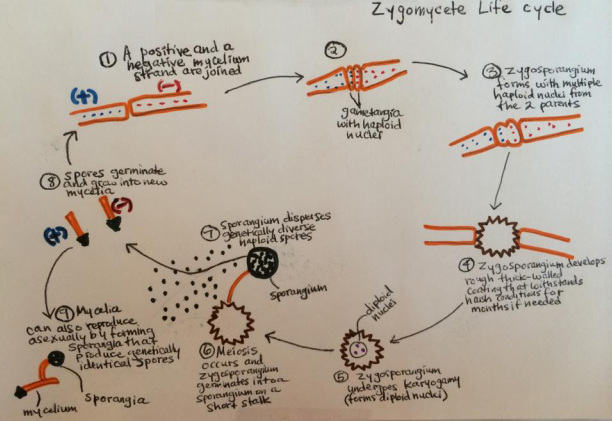
Reproduction(1):
- Sexual and asexual reproduction
- Asexual is more frequent
- Whether one mode of reproduction is chosen over the other is dictated by environmental conditions
- Spores are usually dispersed in hot dry weather
Conservation Status(1):
- Spores are very common in the air, can grow anywhere that supports its growth (moist environment with sugar or starch)
Interesting Facts(1):
- Produces steroids such as Progesterone that make it able to be used in common birth control pills
- Most common and fastest growing of the Zygomycota
- The spores are usually dispersed in hot dry weather and contain allergic proteins, may cause respiratory and nasal symptoms in humans (coughing, chest discomfort and allergic reactions)