Classification:
 pic (2)
pic (2)
Natural History:
Habitat:
- Found in agricultural settings, precipitation(rain and snow), alpine streams/lakes, wild plants, epilithic biofilms from rivers outside of agricultural zones (5)
- Most strains live on (phyllosphere), therefore it is an epiphytic bacterium (6)
- Phyllosphere considered extreme environment for bacteria due to constantly changing conditions (6)
- Thrive in cool wet conditions: rain is essential to survival and transport to new hosts (6)
- Hot dry weather causes dramatic population decrease (6)
Metabolism:
- Aerobic metabolism (6)
- Chemoheterotrophic organisms that depend on host organism for nutrients (6)
- Nutritionally versatile: thrives on damaged plant tissues and colonizes the surface of plant leaves (6)
- Get nutrients from those that diffuse onto leaf surface (6)
- Can also live as saprophytes (live off dead organic material) when conditions are not favorable for pathogenic existence (6)
Reproduction:
Pathology:
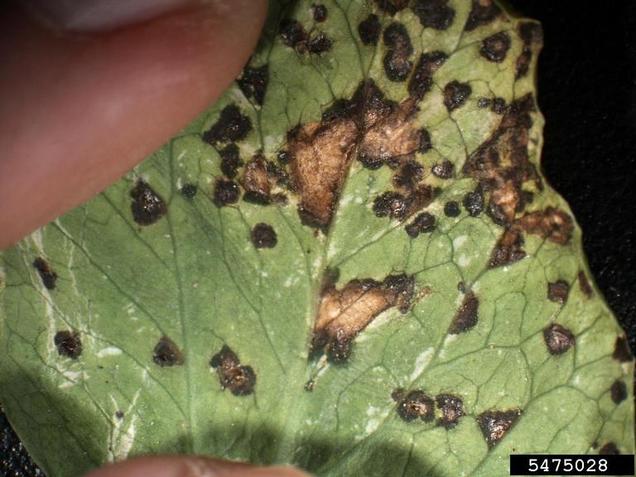
- Pseudomonas syringae is a plant pathogen, able to infect a wide range of plants species and exists as over 50 different pathovars (each is specific to a particular plant) (4)
- Produces Ina proteins that cause water to freeze at fairly high temperatures, causing injury to plants (4)
- Disease due to the bacteria is not merely due to its presence but its overpopulation on the surface of the host (6)
- Pathogenic strains enact disease symptoms by releasing toxins and enzymes that degrade cell walls (6)
- Adapts to unfavorable weather conditions by forming lesions on the host (these signify pathogenic activity) (6)
- As the bacteria flourishes in the host, it causes disease, lesions and frost damage; therefore leading to its own demise (6)
- Many strains are pathogenic but some are not and can be used as potential inoculations against the bacteria for some plants (6)
Conservation Status:
- Found in nature and in agricultural settings, not in any way endangered (5)
Interesting Facts:
-Ski resorts exploit these surface proteins to induce the creation of artificial snow
- Has ice nucleation properties: produces surface proteins that are necessary to ice crystal formation at sub-zero temperatures on plant surfaces (6)
-Ski resorts exploit these surface proteins to induce the creation of artificial snow

