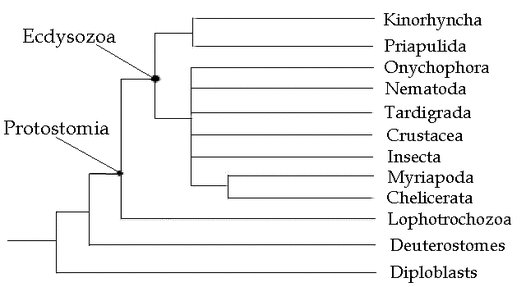
 Ecdysozoa Phylogenetic tree (7)
Ecdysozoa Phylogenetic tree (7)
Description:
- Protostome (4)
- Free-living benthic marine worms with an eversible proboscis (3)
- Range in size from 1 mm (early instars may be as small as 50 µm) to more than 40 cm in length (3)
- The body is cylindrical and includes an introvert that includes spines (retractable and invertible proboscis), a neck-like collar, a trunk, and sometimes a "tail" (3)
Nutrition(3):
- Feed on soft-bodied invertebrates such as polychaete worms and other priapulans
- While feeding, a portion of the toothed pharynx is ejected through the mouth at the end of the extended introvert, then retracted together with the prey item
Habitat(3):
- Found from polar seas to the tropics and from ocean trenches to the intertidal zone
- Burrow actively in relatively fine marine sediments, primarily in boreal and cold temperate seas, burrow or live interstitially among sediment particles
Reproduction(3):
- Separate sexes
- Males spawn first, then females; fertilization is external
- Nearly all species have a non-swimming benthic larval stage, which may last as long as one to two years
- Larvae live in mud and are probably detritivores

