 Diplomonad tree (5)
Diplomonad tree (5)
Description(1):
- A flagellated, microaerophilic microorganism
- Member of Excavata(4)
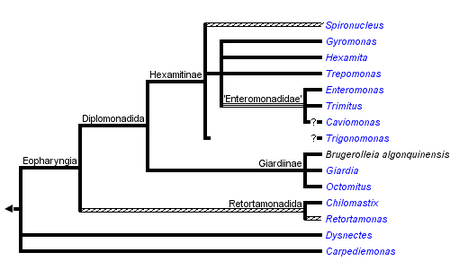
- A diplomonad(4)
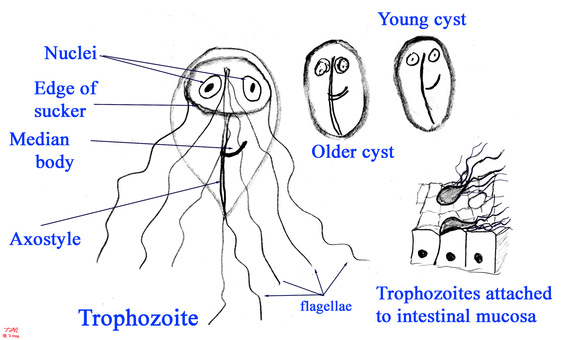
- Pear-shaped and has two identical nuclei, a ventral disc for adhesion to the host intestine, and flagella
- Infect human, mammals, reptiles, and birds, cows, sheeps and pigs
- The cyst is highly resist against chlorination and ozonolysis
- Giardiasis is the clinical manifestation of G. lamblia infection; characterized by severe diarrhea, malnutrition weight loss, and slight intestinal epithelial injury
Habitat(1):
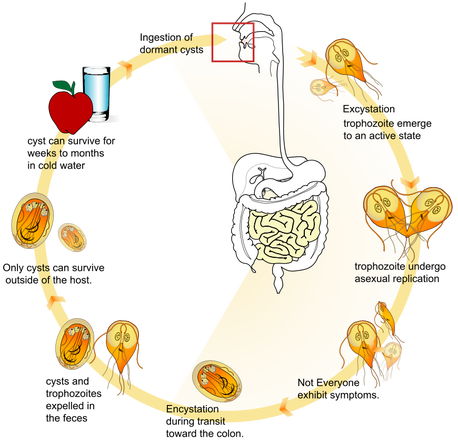
- Can survive in cold water between 4~8 degrees Celsius
- Often found in contaminated water and feces of infected individual
- The trophozoite form is the vegetative form of G. lamblia, and is found in the small intestine of infected individuals; may also be found in their feces
Nutrition(1):
- Are microaerophilic
- Lack mitochondria
- Rely on cytochrome-mediated oxidative phosphorylation
- Can perform aerobic and anaerobic metabolism depending on environmental oxygen concentration; predominately rely on fermentation
- Carry out fermentation even in the presence of oxygen
Reproduction(1):
- G. lamblia life cycle consists of two stages: the cyst and trophozoites
- The cyst is the reproductive form, and consists of a protective cyst wall as well as four nuclei
Interesting Facts(1):
- First discovered by Van Leeuwenhoek in 1681, who found it in his own diarrheal stool