Description(3):
- Very large deciduous trees, with an angular crown and long erratic branches
- Leaves are fan-shaped with 2 lobes that turn yellow in autumn, 5-10 cm
Habitat:
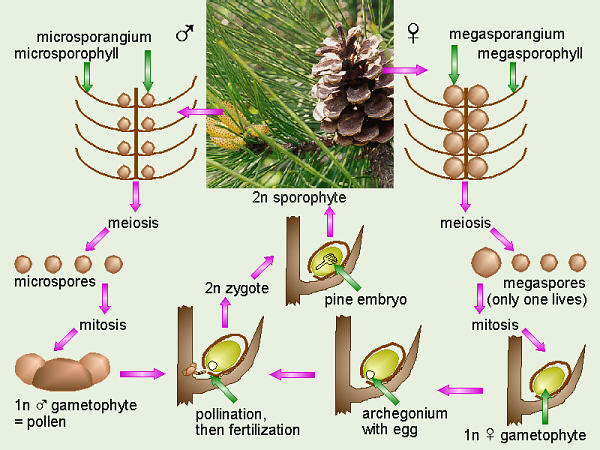
Reproduction(3):
- In flower from April to May
- Seeds ripen from October to November
- Individual flowers are either male or female, but only one sex is to be found on any one plant
- Pollinated by wind
- The tree grows at a slow rate
- Males make fairly inconspicuous reproductive structures, the females make “fruits,” which when ripe, fall to the ground and smell like dog excrement (5)
Interesting Facts(3):
- Long history of medicinal use in traditional Chinese medicine
- Unique species of tree with no close living relatives
- One of the best know examples of a living fossil