pic (2)
pic (2)
Distinguishing Characteristics:
- Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes with tissues that develop from embryonic layers (3)
- Heterotrophs that ingest their food (3)
- Have 3 types of tissue in animals (4):
- Epithelial
- Connective
- Muscular
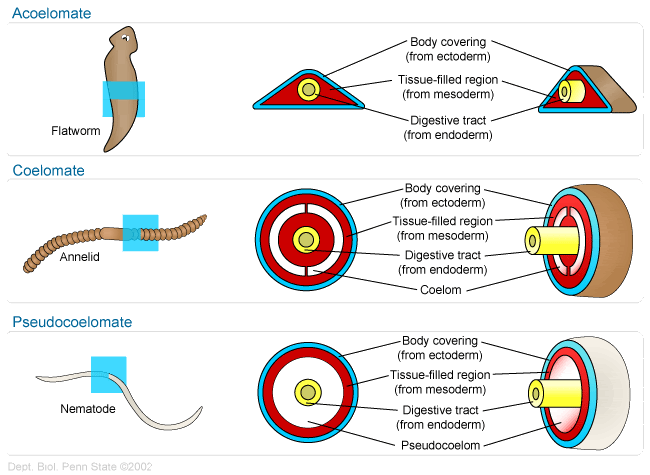
- Body Plans (3):
- Symmetry- ranges from none at all to radial or bilateral, bilaterally symmetrical animals have dorsal and ventral sides as well as anterior and posterior ends
- Tissues- Eumetazoan (does not include sponges and other animals) embryos are diploblastic (2 germ layers) or triploblastic (3 germ layers)
- Body Cavities- (triploblastic animals) may be present or absent, can be pseudocoelom (derived from both mesoderm and endoderm) or true coelom (derived only from mesoderm)
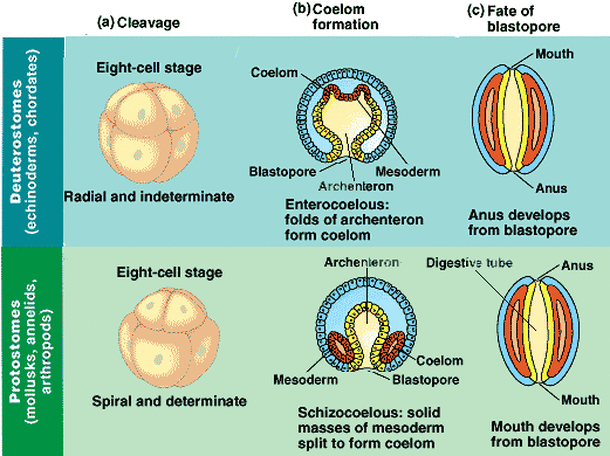
- Protostome and Deuterostome Development- differ in patterns of cleavage, coelom formation, and fate of the blastopore
Embryonic Development(4):
|
Protostomes:
|
Deuterostomes:
|