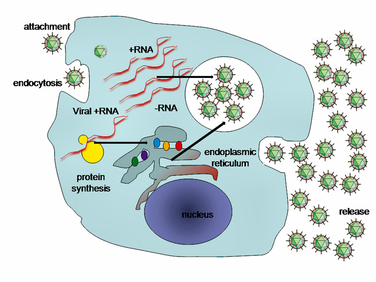
 (9) common viral replication cycle
(9) common viral replication cycle
-Lytic cycle (11)
- The virus inserts its DNA into the host cell
- That DNA will move into the nucleus
- The machinery of the host nucleus replicates the viral DNA
- The viral DNA makes copies of itself called mRNA
- Each of the mRNAs go to a ribosome and influence the ribosome to create proteins that the virus needs
- The viral proteins assemble into new viruses and escape the cell; in the process the lyse the cell
- This happens in multiple cells at the same time; therefore viruses are propagated exponentially
- The genetic material is RNA; it travels along with the enzyme reverse transcriptase
- The virus injects RNA and reverse transcriptase into the host cell
- Reverse transcriptase takes the RNA and makes DNA out of it **the RNA has very high mutation rates (this makes the virus able to evade the immune system by constantly changing)
- The DNA moves into the nucleus then steps 3-7 of the lytic cycle follow (in this case, reverse transcriptase leaves the cell with the newly formed virus upon lysing it)
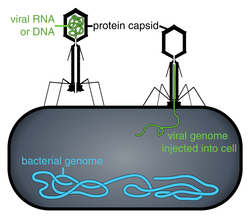 (10) Bacteriophage injecting its genome into bacteria
(10) Bacteriophage injecting its genome into bacteria
-Lysogenic cycle (11)
- The virus injects its DNA into a bacterium
- As the bacteria copy themselves, the viral DNA is also copied over and over
- From this point, the virus can eventually jump back to the lytic cycle
