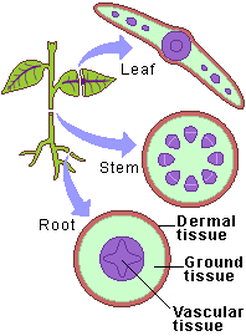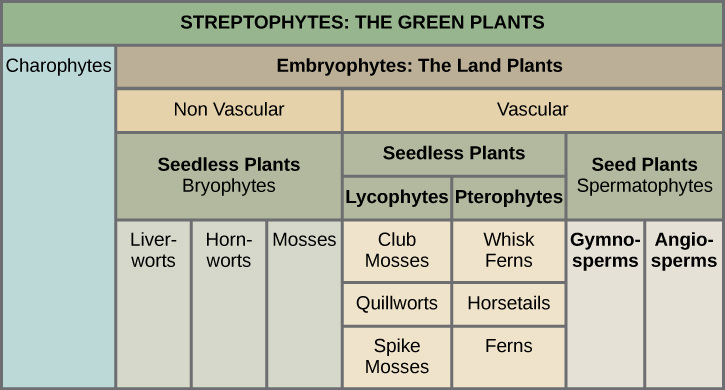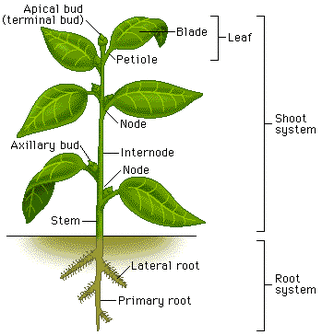
Plant Organs of Most Vascular Plants (11):
pic (10)
pic (10)
- Root: multicellular organ that anchors a vascular plant in the soil, absorbs minerals and water and often stores carbohydrates (also: taproots, lateral roots)
- Stem: organ consisting of an alternating system of nodes and internodes.
- Leaf: the main photosynthetic organ
Plant Tissue (10):
|
Tissue System
and Its Functions Dermal Tissue System • protection • prevention of water loss Ground Tissue System • photosynthesis • food storage • regeneration • support • protection Vascular Tissue System • transport of water and minerals • transport of food |
Component Tissues
Epidermis Periderm (in older stems and roots) Parenchyma tissue Collenchyma tissue Sclerenchyma tissue Xylem tissue Phloem tissue |
Characteristics of the 4 Main Types of Plants:
Nonvascular:
- Thrive in mostly damp habitats (13)
- Nonvascular because they don't have tracheids; instead water and nutrients circulate inside special conducting cells (13)
- The gametophyte is the dominant form (13)
- The sporophyte is dependent on the gametophyte and remains permanently attached for nutrition and protection (13)
- ex) mosses, liverworts, hornworts (13)
Vascular Seedless:
Gymnosperms:
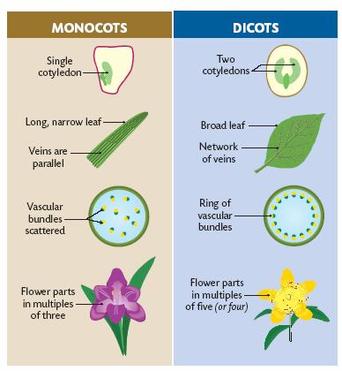
Angiosperms: