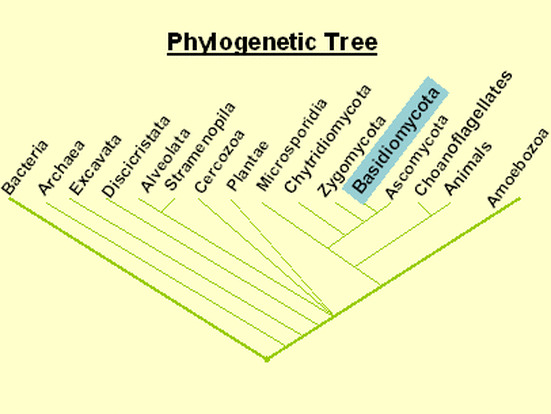
Description(1):
- Decomposes dead organic material
- Usually grows on trees that have broad leaves
- Most commonly found on chestnut trees
- White rot fungus: capable of degrading lignin
- Produce mycelia: responsible for the absorption of nutrients through extracellular digestion
Habitat:
- From eastern Asia, mainly China and Japan(1)
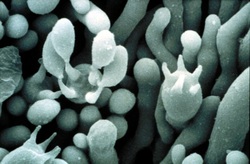 Basidium (1)
Basidium (1)
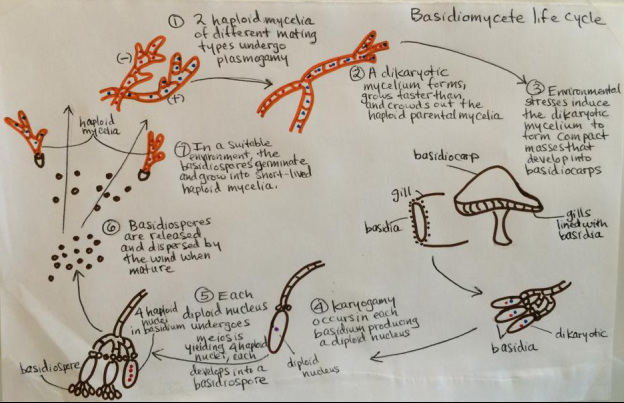
Reproduction(1):
- Produce basidia: basidium is club- shaped and responsible for spore production, spores produced are referred to as basidiospores
- Basidia are where both karyogamy and meiosis take place
- Basidia form on gills and therefore the mushroom cap itself serves as protection for this important reproductive structure
- Once spores are dispersed from the gills and germinate, they form haploid hyphae
- Next, the haploid hyphae find a mating pair, undergo plasmogamy, and are then dikaryotic mycelium
- When conditions are right, the fruiting body of Lentinula edodes will form
- When the two nuclei fuse together, karyogamy occurs
- The nucleus, which is then diploid goes through meiosis: The haploid spores are then in the basidia and can be dispelled by the wind
- From there, the life cycle starts all over again
Interesting Facts(1):
- World's second most cultivated mushroom (after the button mushroom)
- Shiitake mushroom usage dates back to the Ming Dynasty