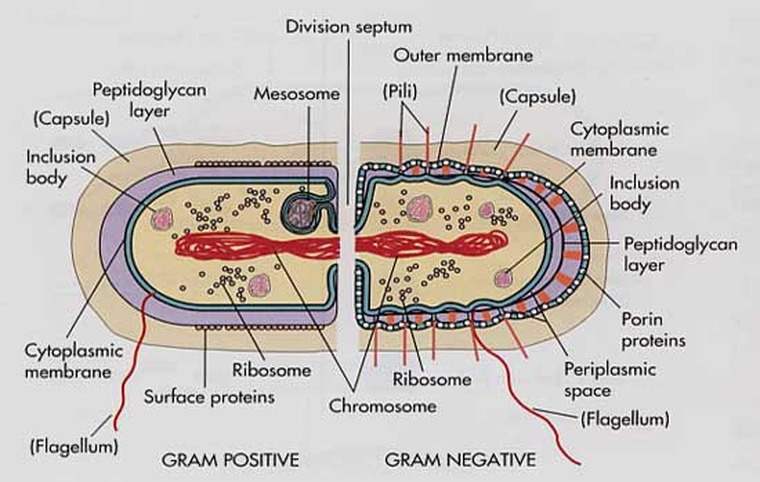
Cell Structure
Cell Accessories
|
Accessory(1)
|
Structure(1)
|
Function(1)
|
Types
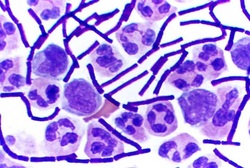
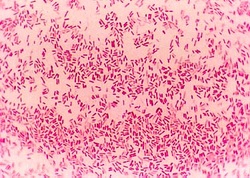
Gram Stain: bacterial staining technique used to distinguish gram positive and gram negative bacteria by the differences in their cell walls (11)
Modes of Nutrition (1)
- photoautotrophy- use photosynthesis to drive synthesis of organic compounds from CO2 or other inorganic carbon compounds
- chemoautotrophy- oxidize inorganic compounds to obtain carbon
- photoheterotrophy- obtain energy from the sun, but must get carbon in organic form
- chemoheterotrophy- consume organic molecules for energy AND carbon