Classification(7):
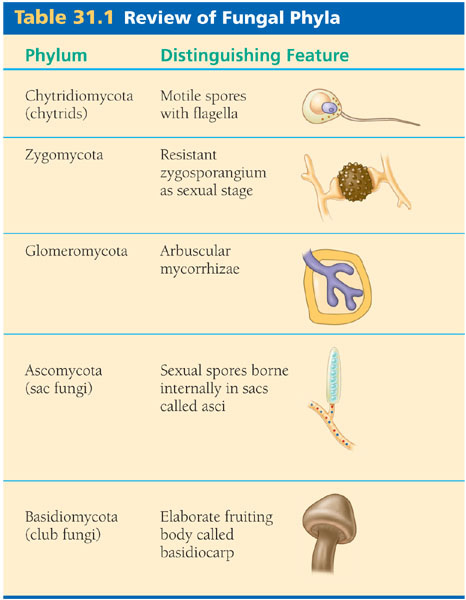
- 5 phyla organized by shape of reproductive structure
- Basidiomycetes- reproductive structures are club-shaped; include mushrooms, mutualists and plant parasites
- Ascomycetes- produce sexual spores in saclike asci, called sac fungi
- Glomeromycetes- form arbuscular mycorrhizae, supply minerals and other nutrients to plant roots
- Zygomycetes- white and fuzzy, include molds, parasitic or commensal symbionts of animals
- Chytrids- decomposers that live in fresh water, known for flagellated spores
Body Form(7):
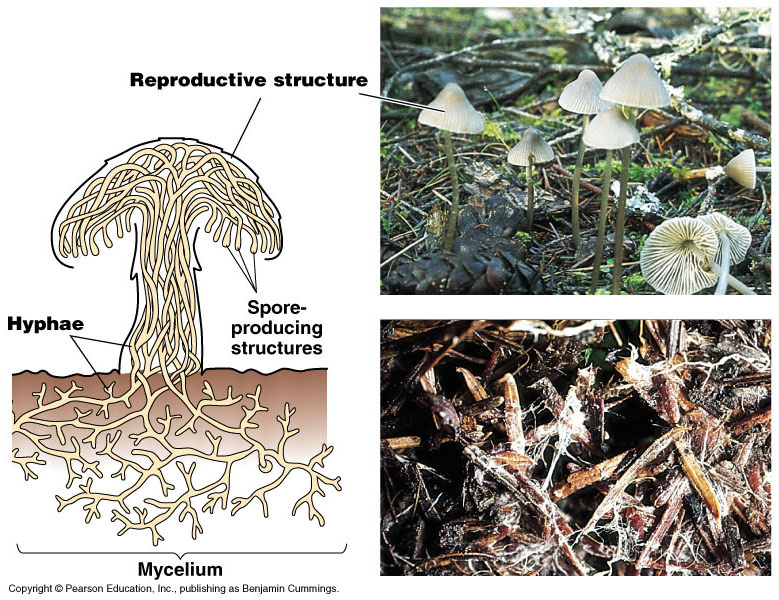
- Made up of a mass of filaments called hyphae
- Mycelium: mat/mass of tangled hyphae (haploid)
- Fruiting body/reproductive structure: only part that has diploid structure
Nutrition:
- Absorb nutrients from living or dead organic matter that they grow on (simple, easily dissolved nutrients) walls(3)
- They give off special digestive enzymes to break down complex nutrients into simpler forms that they can absorb(3)
- Heterotrophic (6)
-Most species of fungi are saprotrophic; they decompose dead matter
- Are the main decomposers of every ecosystem; can break down most organic compounds including lignin (6)
- Store their food as glycogen (6)