Description:
- A calcified red seaweed, a coralline alga (1)
- A jointed or geniculate coralline alga (1)
- The fronds grow in tufts that develop from a flat coralline base (1)
- They are segmented to provide flexibility in seawater and oppositely branched (1)
- Dull purple but its colour can vary depending on the conditions; can appear red, yellow or white when bleached in bright light (1)
- Usually 1 to 12 cm tall (1)
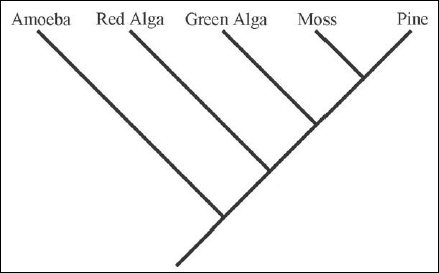
- Classified as Archaeplastida and are most often characterized by the presence of the red pigment phycoerythrin (2)
Habitat(1):
- Distribution is not yet fully known, it occurs in the North Atlantic
- Found in rock pools in the middle and lower shore
- Often forms a distinct zone just below the rim of rock pools
- Also lives on rocks on the lower shore and in shallow water
Reproduction(1):
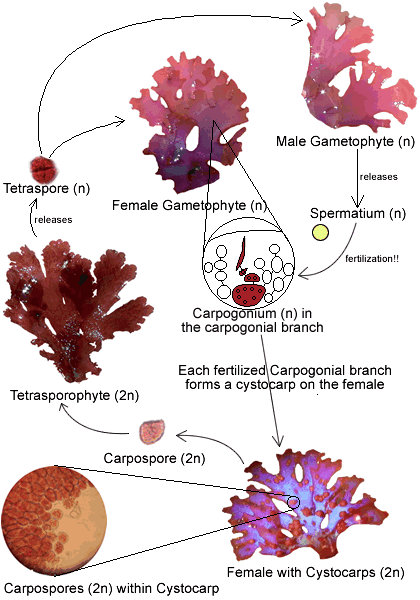
- Male and female reproductive structures are found on separate plants; these structures develop in conceptacles - tiny flask-shaped structures just visible to the naked eye
- After fertilization, diploid spores are released which grow into a phase called the tetrasporophyte
- The tetrasporophytes look just like the male and female plants but they develop conceptacles which contain tetrasporangia
- Each tetrasporangium contains four spores
- When mature, meiosis occurs in the tetrasporangium and haploid tetraspores are released
- The haploid tetraspores grow into male and female plants
Conservation Status(1):
- Common, does not seem to be threatened
- It is unknown how it and its other calcified relatives will respond to ocean acidification
Interesting Facts (1):
- Provides a home for small sea creatures and often has other seaweeds growing on it